A Sustainable Diet: The Best Food Choices for a Healthy Planet

The Importance of a Sustainable Diet
You care about the planet and want to make food choices that are better for the environment. Still, it can sometimes feel overwhelming. What difference can one person really make?
The truth is: a sustainable diet makes a real impact. The food choices you make every day affect not only your own health, but also the health of the planet. By following a sustainable diet, you contribute daily to a healthier world. Even small, sustainable changes in what you eat can lead to meaningful environmental benefits.
At Plants for Health, we help you make sustainable food choices that are practical, evidence-based, and beneficial for both people and the planet.
Eating More Plant-Based: A Core Element of a Sustainable Diet
One of the most important aspects of a sustainable diet is reducing the environmental impact of food production. This includes land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Animal-based protein production currently uses about 83% of global agricultural land, while providing only 18% of total calories worldwide. In addition, animal agriculture requires large amounts of water and produces significant greenhouse gas and nitrogen emissions.
In short, our current food system is not sustainable.
A sustainable diet therefore emphasizes plant-based foods. Choosing plant-based options more often helps reduce emissions, lower land and water use, and limit deforestation and overfishing. These changes benefit both human health and planetary health.
Plant-Based Protein Sources in a Sustainable Diet
Replacing animal-based proteins with plant-based protein sources is one of the most effective ways to reduce your environmental footprint.
Research shows that animal products generate far higher greenhouse gas emissions per kilogram of food than plant-based alternatives. Legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds are especially sustainable protein sources.
Reducing meat consumption is a simple but powerful step toward a sustainable diet:
Meat production accounts for around 27% of greenhouse gas emissions in an average Western diet.
Producing 1 kilogram of meat requires 4–25 kilograms of plant-based feed, along with large amounts of land, water, and energy.
By consuming protein directly from plants rather than through animal products, resources are used far more efficiently.
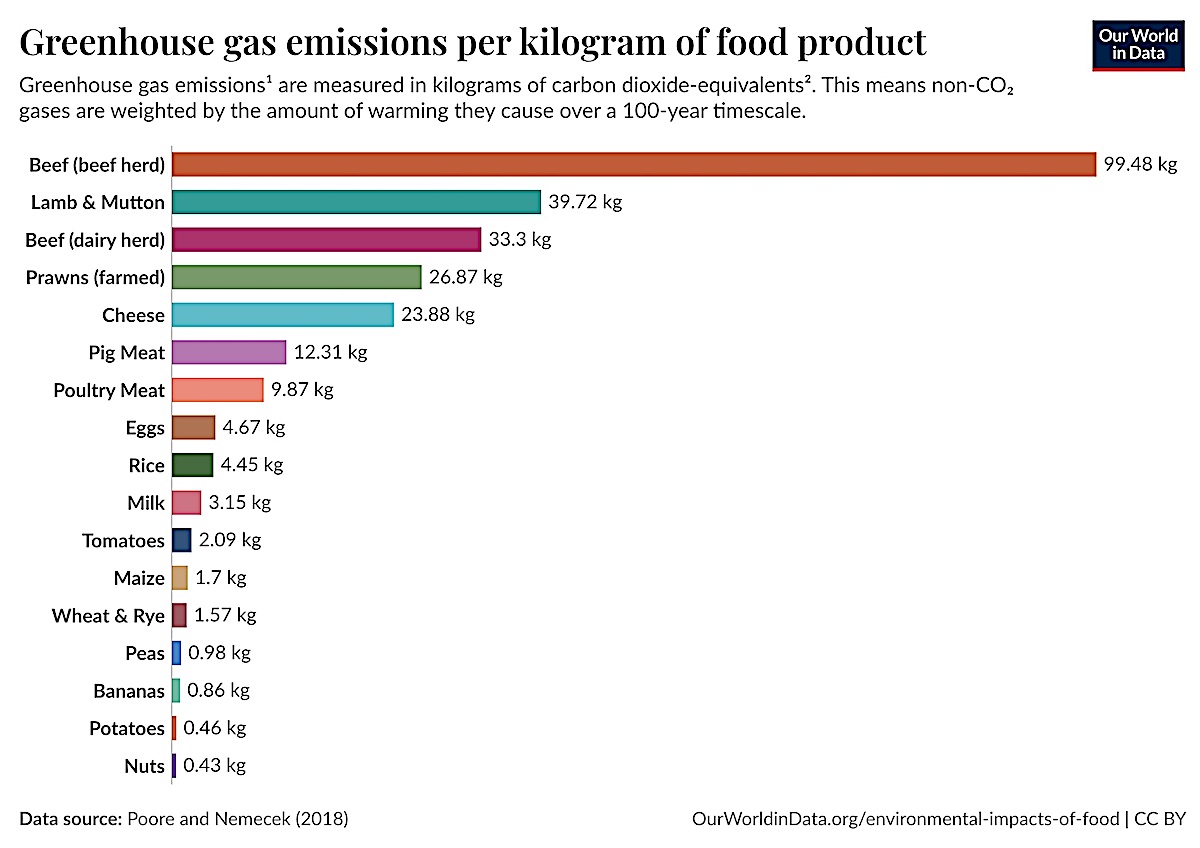
Source: Poore, J., & Nemecek, T. (2018)
Sustainable Diet Choices: Plant-Based Milk Alternatives
A sustainable diet also includes mindful choices around dairy and dairy alternatives.
Producing cow’s milk requires relatively large amounts of land and water and results in approximately three times more greenhouse gas emissions than the production of soy drink.
Plant-based milk alternatives such as soy, oat, or pea drinks are therefore more sustainable food choices and fit well within a sustainable diet.
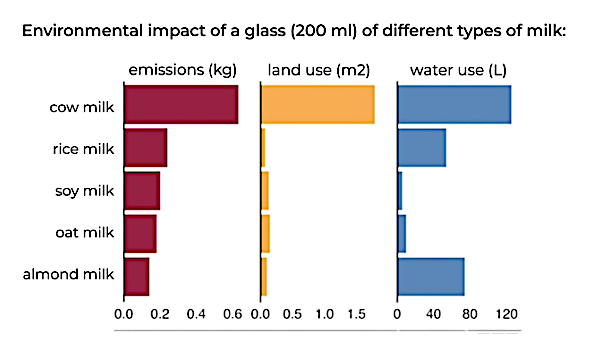
Source: Poore, J., & Nemecek, T. (2018)
A Sustainable Diet Also Means Reducing Food Waste
Globally, nearly one-third of all food produced is wasted. Food loss occurs throughout the entire supply chain, from production to consumption. This not only wastes food but also the water, energy, and land used to produce it.
Reducing food waste is therefore an essential part of a sustainable diet.
Practical Tips to Reduce Food Waste
- Use frozen vegetables and fruit
They are just as nutritious, more affordable, and have a longer shelf life. - Turn leftovers into meals
Soups, stews, and stir-fries are perfect for using vegetables, legumes, grains, and herbs that might otherwise be discarded. - Don’t immediately throw away foods past their best-before date
Many shelf-stable products remain safe to eat. Always check using sight, smell, and taste.
The Sustainable Diet and Planetary Health
The updated EAT-Lancet Commission report (2025) reinforces the same conclusion as the original 2019 report: the greatest benefits for both human health and the environment come from a predominantly plant-based diet.
The Planetary Health Diet provides a clear framework for a sustainable diet. It is:
- scientifically supported
- nutritionally balanced
- environmentally sustainable
- adaptable to different cultures and preferences
In practice, this means focusing on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while limiting red meat, ultra-processed foods, and added sugars. Small amounts of dairy, fish, eggs, or poultry can be included but are not essential.
Making Sustainable Food Choices Together
At Plants for Health, we understand which dietary changes have a large impact on both health and sustainability.
We can support you step by step in making practical, achievable food choices that fit your lifestyle and contribute to a healthier planet. The good news is that the foods that best support your health are often also the most sustainable, a true win-win.
Learn more about our lifestyle program here, in which we help you build a healthy and sustainable diet.
Sources
- Milieu Centraal. (z.d.). De milieu-impact van vlees. Via: https://www.milieucentraal.nl/eten-en-drinken/milieubewust-eten/de-milieu-impact-van-vlees/
- Scarborough, P., Clark, M., Cobiac, L., Papier, K., Knuppel, A., Lynch, J., Harrington, R., Key, T., & Springmann, M. (2023). Vegans, vegetarians, fish-eaters and meat-eaters in the UK show discrepant environmental impacts. Nature food, 4(7), 565–574.
- Poore, J., & Nemecek, T. (2018). Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science (New York, N.Y.), 360(6392), 987–992.
- Rockström, J., Thilsted, S. H., Willett, W. C., Gordon, L. J., Herrero, M., Hicks, C. C., Mason-D’Croz, D., Rao, N., Springmann, M., Wright, E. C., Agustina, R., Bajaj, S., Bunge, A. C., Carducci, B., Conti, C., Covic, N., Fanzo, J., Forouhi, N. G., Gibson, M. F., Gu, X., … DeClerck, F. (2025). The EAT-Lancet Commission on healthy, sustainable, and just food systems. Lancet (London, England), 406(10512), 1625–1700.
You might also find this interesting:

Did you find this article helpful? Would you like to work with the experts at Plants for Health on improving your health? Our lifestyle program provides tailored guidance, practical tools, and evidence-based strategies shown to be effective. So you can make lasting changes to your lifestyle.
